Institute of Natural Sciences
Interface between the disciplines
The central task of the Institute of Natural Sciences is applied research and the provision of courses, e.g. in mathematics and physics. The Institute is an important interface between the various engineering and economic disciplines. Applied natural sciences form the basis of a wide range of disciplines. Applied natural sciences form the basis of a wide range of disciplines such as electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, economics and computer science.
This is particularly evident in the networking of the Institute of Natural Sciences with other areas of the university. For example, in the specific collaborations with the Departments of Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Energy Systems, Computer Science, Economics and Measurement and Sensor Technology.
Research profile
The focus of the institute and its applied research lies in the fields of physics and chemistry as well as mathematics and safety engineering.
This broad subject focus makes the Institute of Natural Sciences an important interface between the various disciplines. There are research links to the other institute of the Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences.
Fields of research
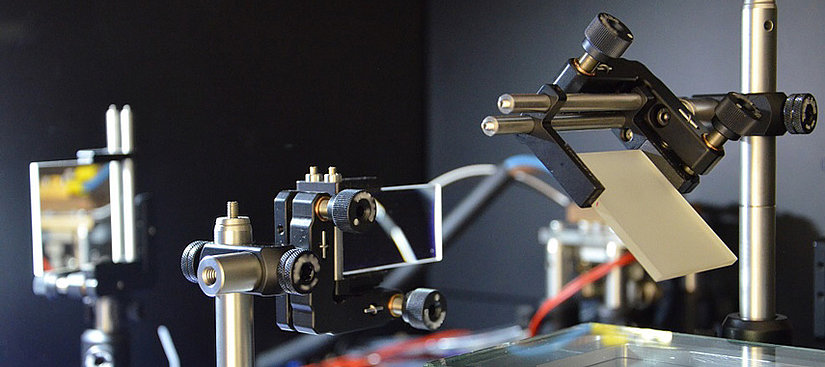
The practical application of physics and chemistry in the Institute of Natural Sciences is primarily found in optoelectronics, and microsystems technology. In the field of optoelectronics, the focus is on semiconductor lasers. The radiation behavior and beam quality of these components are analyzed using wavefront measurement and compared with simulations. Organic semiconductor lasers form the bridge to microsystems technology. The elective subject Microtechnology teaches manufacturing processes and functional principles of semiconductors and the other microsystems (e.g. microfluidic systems). The laboratory enables students to design and produce microsystems in student projects. Within the didactics of physics, concepts are developed to promote problem-solving strategies as part of the physics exercises.
In the mathematical didactic research, for example, one doctoral project is investigating the effectiveness of interactive learning videos on error patterns that frequently occur in basic mathematics. Another project is investigating the transfer of flexibility. This involves transferring alternative solution strategies to different types of tasks.
In the field of data science, mathematicians at the Institute of Natural Sciences deal with a wide variety of aspects: In addition to dara analysis using wavelets and the analysis of large measurement data from sensor technology, optimal algorithms are developed using Quasi Monte Carlo methods. Learning analytics methods are also used in mathematical didactics. Questions of insurance and financial mathematics are also considered as a concrete field of application for data science.
Another focus of mathematical research is the theory and application of dynamic systems: These play a central role at the Institute of Natural Sciences, for example in the modeling of thermodynamic or rotating systems. This includes the use of non-linear methods to improve vibration analyses. In addition, applications of dynamic systems within mathematics are also considered, such as applications in the theory of uniform distribution (ergodic theory, Quasi-Monte Carlo methods) as well as non-hyperbolic dynamic systems and complex dynamic systems (iteration of rational functions).
In safety engineering, research activities focus on reliability and functional safety. In functional safety, for example, the optimization of safety concepts in fire detection technology and the investigation of mechanical influences on safety-relevant hardware components on electric motors are the scientific focus.
